Hi friends,
This is very small post about Event receiver in SharePoint. When we
create event receiver we have lot of options to select which type of event
receiver we want to create. We can create event receiver for SharePoint site,
List and libraries and workflow. Here I
am mostly focusing on different list template id and how can we trigger an
event for a particular list and library.
To create event receiver we need to perform following
steps:
è
Select SharePoint
Project template->2010->Event receiver. Type proper name for event
receiver and select .net framework 3.5 because SharePoint 2010 is built on top
off .NET framework 3.5.
è
Type your Site Url and
select deploy as sandbox solution
è
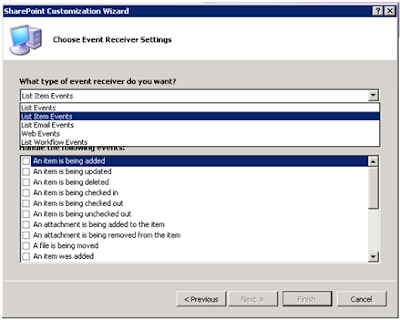
Here we have different
types of event receiver as shown bellow. We can create event receiver for List
Events, List Item Events, List Email Events, Web Events and List workflow
events.
è
If we want to create
list type event receiver then we have many set of events related to SharePoint
List. Bellow are list of events related to SharePoint list.
è
If you select”List
Item Events” then you have another options available which shows about the
event source. Below are many event source list such as custom list,
announcement list, contact list etc..
è
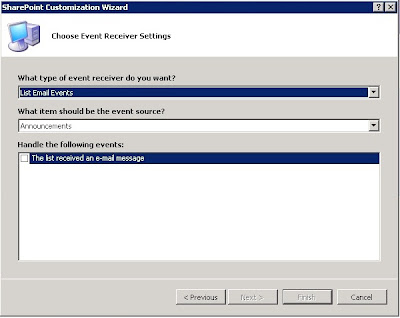
If you select “list Email Events” then you can send
mail to user when any operation is performed on list. Here also we have event
source and some events related to source.
è
If you select “Web Event” type event then you have
only event related to web.
è
Here we will create
List Item events and we will chose Custom List as event receiver and select
related events which needed.
è
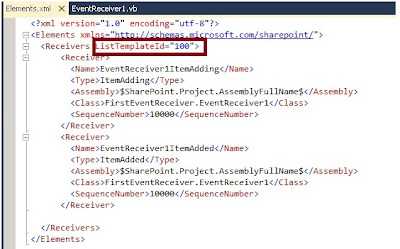
You can check that It
shows ListTemplateId=”100” based on different event source SharePoint has fixed
ListTemplateId for each.
è
Now suppose we want to
execute this event receiver to a particular list which is type of custom list
we can set ListUrl of that list as show below
è
As shown below this
event receiver will execute only for list MyListName.
Like this way we can execute event receiver for any document library and web
site.
è
If you changed name of your event receiver from
solution explorer then you also need to change tags inside Element.xml file otherwise
event will not fire for event receiver. So wherever EventReceiver1 exist in Element.xml
change it with your new name.
Types of Event in Event Receiver:
è Before
Events (Synchronous): The
before events are those that happen just after the event occurred, but before
SharePoint writes any data to the SharePoint content database. Such events are
useful for custom validation, rules checking, and cancellation of users’
actions.
è After
Events (Asynchronous): The
After events are those that happen after SharePoint commits the data to the
SharePoint content database. These “After” event handlers cannot cancel the
current action/operation, but they are guaranteed to execute only after
specific actions.
Before
events run in the same process and thread as the current action, while After events by default run in a
background thread; however, you can force them to run synchronously, that means
within the same process and thread of the current action.
è
Below list shows ListTemplateId for all
SharePoint list and libraries.
ListTemplateId
|
Description
|
100
|
Generic list
|
101
|
Document library
|
102
|
Survey
|
103
|
Links List
|
104
|
Announcement list
|
105
|
Contact List
|
106
|
Event List
|
107
|
Task List
|
108
|
Discussion Board
|
109
|
Picture Library
|
110
|
Data Source
|
111
|
Site Template Gallery
|
112
|
User Information List
|
113
|
Web Part Gallery
|
114
|
List Template Gallery
|
115
|
Xml Form Library
|
116
|
Master page Gallery
|
117
|
No-Code Workflows
|
118
|
Custom Workflow
Process
|
119
|
Wiki Page Library
|
120
|
Custom Grid for list
|
130
|
Data Connection Library
|
140
|
Workflow History
|
150
|
Gantt Tasks list
|
200
|
Meeting Series list
|
201
|
Meeting Agenda list
|
202
|
Meeting Attendees
list
|
204
|
Meeting Decisions list
|
207
|
Meeting Objectives
list
|
210
|
Meeting text box
|
211
|
Meeting Things To
Bring list
|
212
|
Meeting Workspace Pages list
|
300
|
Portal Sites list
|
301
|
Blog Posts list
|
302
|
Blog Comments list
|
303
|
Blog Categories list
|
1100
|
Issue tracking
|
1200
|
Administrator tasks list
|
2002
|
Personal document
library
|
2003
|
Private document library
|
è
You can select or type any one of the template Id
in your event receiver to work for template specific.
This post is also related to:
How to create list specific Event receiver
in SharePoint
Different List Template Id in SharePoint
2010
SharePoint List , Document library and
Internal Id
Regards
Gireesh Painuly
Happy Coding ...